You’ve heard the phrases I need SEO and Let me Google that for you too many times to count, but what exactly are these two buzzwords? SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization, while Google’s Algorithm refers to how Google operates its search engine. Fortunately, the folks at Google have made public much of the algorithm that drives their search results, which means you can use this information to optimize your website.
Optimizing your website for the search engines
Knowing how to optimize your website for search engines is a valuable skill that will help you bring in new customers. You may already be running AdWords, but you might be doing it wrong. The Web makes information about search engine optimization easy to find, so if you have a business website and aren’t making an effort to increase your rankings in Google or Bing, you may be hurting your traffic. Use these tips as your guide to learn more about optimizing your site for search engines.
Optimize for long-tail keywords
Long tail keywords are more specific, and therefore are searched less frequently. Because of their low search volume, long tail keywords will not produce enough traffic to your website on their own. That’s why you need to optimize for long tail keywords by using numerous different phrases, synonyms and related terms with your main keyword. An example would be if you were optimizing for a keyword phrase such as Small office furniture instead of just office furniture or office supplies. You could also use longer terms such as Desk accessories for home offices or even home offices supplies, which adds additional keywords without being too obvious about it.
Properly categorize your blog posts
Categorizing your posts is important for two reasons. First, it helps people find you when they’re searching on particular topics (and you want to be found). And second, categorizing is an easy way to help new visitors know what they’re in for if they stick around and read. Your categories can include industry-specific jargon, so long as that makes sense to your audience; someone selling construction equipment doesn’t need a breakdown of frequently asked questions about civil engineering.
Be as precise or broad as you think will work best for your audience; just don’t leave them out altogether! Make sure all your links are relevant and useful: This might seem like common sense, but it happens more often than you might think. It also doesn’t mean every link has to go somewhere helpful—in fact, some of your most engaging content may come from stories that have nothing at all to do with your business—but each link should have some relevance to something on your site.
If you ever wonder whether a link is useful enough, err on the side of caution by removing it instead of leaving it up without purpose. Encourage comments by replying yourself: Many bloggers forget how powerful their own voice can be in encouraging engagement from readers.
Write naturally, but use key phrases
To ensure your content is read and shared, try to pepper it with keywords that search engines value. By using a tool like SEMrush or SpyFu, you can find out what phrases people are searching for online. This will give you an idea of what kind of content they’re interested in, which can help inform your writing and improve your click-through rate (CTR). See how writers at BuzzFeed effectively use keywords to drive traffic to their posts.
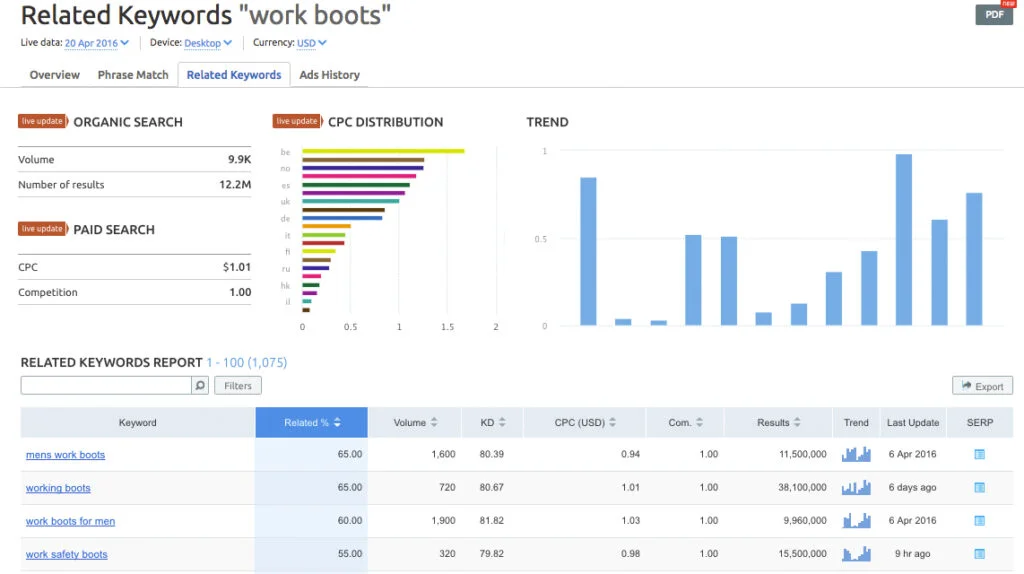
Rather than just including key phrases throughout a post, though, sprinkle them into subheads and bolded text to attract attention. If you’re not sure how many times you should use each phrase, aim for about three mentions per paragraph but no more than five. It’s also important to make sure you include a variety of relevant terms rather than repeating one over and over again. Use tools like Google Trends or Keyword Planner to determine which words and phrases are most popular now.
You can also look at competitors’ sites to see what terms they tend to use most often. Make sure your keyword density isn’t too high—Google penalizes sites with a higher ratio of keywords than normal language—but don’t be afraid to go overboard either; some people recommend as much as 10 percent for some industries. The best way to know if you’re doing it right? A good keyword density checker will tell you exactly how many times you’ve used certain words, so be careful not to get carried away while checking yours!
Target users, not search engines
There are two main ways to approach your site’s content: You can target people or search engines. Google’s algorithm for search engine optimization (SEO) is known as a black box, which means that no one outside of Google really knows how it works. But by doing some reverse engineering, you can make educated guesses about what search engines like. Once you know what users want, you can also tailor your content so that it keeps them happy and coming back for more! After all, great sites are made with love – and love comes from deep understanding of their users. So how do you dig into their minds? By starting with a bit of competitive research.
Use tools like SEMrush to see what keywords your competitors rank for in search results. Then figure out why they rank there, and use those insights to create an even better version of that page on your own site. That way, when someone searches for something similar to what you offer, they’ll find yours first!
Create an XML sitemap.xml file
XML Sitemaps provide you with an easy way to submit sitemaps to search engines. There are a number of free tools available online that allow you to create a site map file, including SEOToolSet and XML Spy. Once you have created your sitemap, visit Webmaster Tools (Google) or any other search engine’s site to verify that it has been submitted properly. If search engines can’t find your pages, they won’t include them in their search results, which is why it is critical for you to do all you can to ensure that sites have been properly submitted and linked.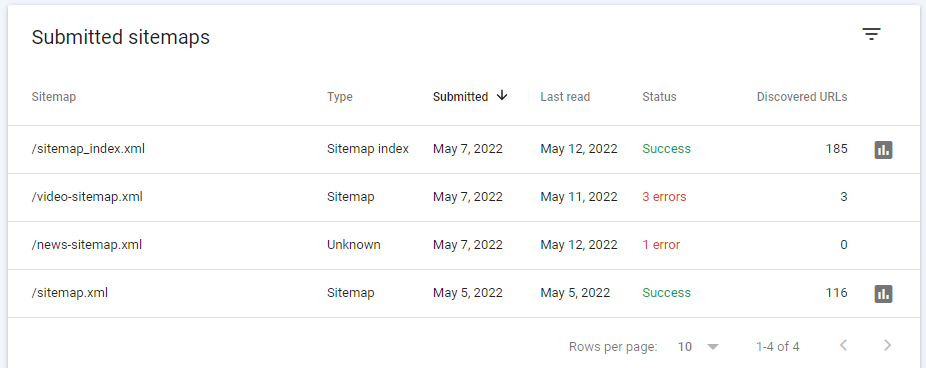
These additional efforts can go a long way toward improving your overall rank and ensuring that traffic keeps coming through natural sources. After you have verified that your XML sitemap has been added to Webmaster Tools, start submitting it regularly on a weekly basis so that search engines will be able to keep up with changes on your website.
You should also consider updating it whenever you make significant changes such as adding new content or changing existing content. This will help ensure that these updates get picked up by search engines quickly so as not to cause negative effects on user experience. As such, many marketers recommend updating your sitemap once every two weeks at minimum while others recommend doing so every week.
Be sure to use H1 tags appropriately
It’s important to note that, while HTML best practices are important for both visitors and search engines, they aren’t intended to trick search engines. For example, keywords in an H1 tag aren’t as impactful on a website’s ranking as you might think. In fact, some major search engines don’t even include H1 tags when assessing a site for ranking potential. While it’s important to be aware of these guidelines, it’s also vital not to misuse them.
Use an effective header tag structure
Headers help define structure, but many brands don’t know how to use them properly. Poorly used headers can be a distraction and make your content harder to read. The best way to use headers is to ensure they’re using H1 through H6 tags in conjunction with one another, with each tag only appearing once per page. When designing a new site or revamping an existing one, consider making each section have its own header so it’s easy for users to identify where they are at all times. This will help deliver exactly what your audience is looking for—and ultimately what you want them to see—when they go to your website.
Give each page its own URL slug
Each page of your site should have its own individual URL slug. While you may be tempted to give multiple pages on your site variations of a single URL slug, such as how-to/some-topic, you’re better off giving each page its own unique name. This is what will tell search engines (and your visitors) that it’s an entirely different piece of content and one that deserves to be found and read by people searching for it. And if you do use descriptive URL slugs, like how-to/some-topic that include several words from within your page, make sure they are written in a way that they still convey a message to visitors even when they’re stripped out by search engines.
Link in natural ways
Most web crawlers will only check an image’s alt attribute when it is present on a page. If you decide to include an image, be sure that alt attribute has relevant keywords or descriptions in it to help search engines associate your content with what a reader might look for. That being said, don’t overdo it and use thousands of words for each image; keep them to 150 characters or less. It’s important to note that search engines don’t always like highly optimized images; too much text can actually bring down rankings rather than improve them.
Don’t overdo it with the alt attribute (alt=image name)
When it comes to alt attributes, more is not better. If you’re using a single image as an alternative text replacement for multiple links, don’t add that link text to your alt attribute. Instead, add a title attribute and use each individual link as its own piece of alternative text. You can also use JavaScript to dynamically change your alt attributes when a user clicks on your link—but take care that these replacements are never blank because search engines hate null alt attributes.
conclusion:
To recap, there are five main components of search engine optimization. Content, links, keyword research, user experience and technical setup (think crawlability). If you’re just starting out with your website or have an existing site that isn’t performing well in search results then be sure to address these issues. You can do so by working on your content and links in addition to making sure you deliver a great user experience for search engines that visits your site. The more relevant information you have on your site and how it is presented will also help improve your rankings. The bottom line is that optimizing your site for search engines requires planning and attention to detail, but it’s something anyone can learn how to do.




